Chapter 8: Security
Contents
8.1 Overview of PDF Security
A secure PDF is a document that imposes a set of restrictions on this document’s user, such as requiring a password on opening, or preventing copying/pasting of the document’s content.
There are two aspects to the standard (or built-in) PDF security: password protection and permission flags.
8.1.1 Password Protection
When a secure PDF is created, the document author supplies two secret strings: the Owner and User passwords. Applying these two passwords to the document using an algorithm described in Adobe PDF specifications produces a secure document.
A secure PDF’s content is encrypted with the RC4 algorithm, a stream cipher invented by Ron Rivest of RSA Security. Either a 40-bit or 128-bit key can be used. As of AspPDF.NET 2.2, the 128-bit Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) cipher is also supported, and as of AspPDF.NET 3.5.0.33933, 256-bit AES is supported as well.
To open an encrypted document, the viewer must specify either the user or owner password. Specifying the valid user password enables a user to view the document, but also makes her subject to the permission flags associated with the document. For example, a user may not be able to modify or print the document. Specifying the valid owner password gives the user full control over the document: not only can she view it, but also change or remove its security settings.
An empty string is a perfectly valid value for either password. There are 4 possible password use scenarios:
Scenario 1: Both user and owner passwords are non-empty and not equal to each other.
Scenario 2: The owner password is non-empty, the user password is empty.
Scenario 3: The owner password is empty, the user password is non-empty.
Scenario 4: Both the owner and user passwords are empty.
Version 4.0 and earlier of the Adobe Acrobat family of products supported 40-bit encryption, and recognized the following four permission flags:
- Bit 3: Print the document;
- Bit 4: Modify the document, except by operations controlled by Bit 6;
- Bit 5: Copy/extract content;
- Bit 6: Add and change annotations, fill in form fields, and if Bit 4 is also set, create or modify interactive form fields.
This version of security specifications is referred to as Revision 2.
Adobe Acrobat 5.0 and higher allowed both 40-bit and 128-bit encryption, and introduced a more granular permission system. The new version of security specifications is referred to as Revision 3. The following permission flags are used in Revision 3:
- Bit 3: Print the document, possibly not at high-resolution depending on Bit 12;
- Bit 4: Modify content of the document by operations other than those controlled by Bits 6,9, and 11;
- Bit 5: Copy/ extract content by operations other than those controlled by Bit 10;
- Bit 6: Add and change annotations, fill in form fields, and if Bit 4 is also set, create or modify interactive form fields;
- Bit 9: Fill in existing interactive form fields, even if Bit 6 is clear;
- Bit 10: Extract text and graphics (in support of accessibility to disabled users)
- Bit 11: Assemble the document (insert, rotate, or delete pages, and create bookmarks or thumbnail images), even if Bit 4 is clear.
- Bit 12: Print the document to a representation from which a faithful digital copy of the PDF content could be generated. When this bit is clear (and Bit 3 is set) printing is limited to a low-level representation of the appearance.
8.2 PdfDocument.Encrypt Method
To make a PDF document secure with AspPDF.NET, all you have to do is call the Encrypt method of the PdfDocument object. This method accepts 4 arguments, all optional: the owner password, user password, key length, and permission flags.
The owner and user password arguments are empty strings by default. To avoid Scenario 4 described above, you should set at least one of the passwords, or both, to non-empty strings. Specifying identical strings for both passwords will result in the owner password being ignored.
For RC4 encryption, the key length argument must be set to either 40 or 128. The default value is 40 but 128 is strongly recommended. For AES encryption, the value must be -128 (negative 128) or -256 (negative 256). The negative sign specifies AES as opposed to RC4. AspPDF.NET version 3.5.0.33933 or higher is required for 256-bit encryption.
The permission flags argument should be set to a bit-wise combination of the permission flag constants defined by the AspPDF.NET component. These constants are:
pdfFull = &HFFFFFFFC (all significant bits)
pdfPrint = &H04 (Bit 3)
pdfModify = &H08 (Bit 4)
pdfCopy = &H10 (Bit 5)
pdfAnnotations = &H20 (Bit 6)
pdfForm = &H0100 (Bit 9)
pdfExtract = &H0200 (Bit 10)
pdfAssemble = &H0400 (Bit 11)
pdfPrintHigh = &H0800 (Bit 12)
The default value for the permission flags argument is pdfFull.
To use the permission flag constants in VBScript, you must include a METADATA tag in your .asp file referencing the AspPDF type library (outside the <% and %> brackets). In C#, the type name pdfPermissions has to be put in front of the constant names.
objDoc.Encrypt( "abc", "xyz", -256, pdfPermissions.pdfFull & (~pdfPermissions.pdfModify) );
...
objDoc.Encrypt( "abc", "xyz", -256, pdfPermissions.pdfFull And (Not pdfPermissions.pdfModify) )
...
The code sample 08_encrypt.asp/.aspx (not shown here) is almost identical to the Hello World sample used in Chapter 3, except that it also calls the Encrypt method. The string "abc" is used for the owner password, "xyz" for the user password, -256 for 256-bit AES encryption, and no-printing/no-changing for the permission flags.
Click the links below to run this code sample:

You will be prompted to enter a password when opening this document in Acrobat Reader. You can either enter abc or xyz. Adobe Reader will show a padlock icon on the left-hand side indicating that the document is encrypted.
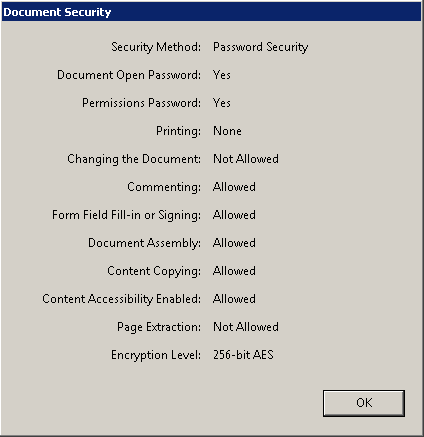
If you click on the padlock icon and select Permission Details, the Document Security dialog box comes up showing the permission details of the document:
8.3 Digital Signing
A digital signature protects a document's integrity and provides proof of the signer's identity. AspPDF is capable of adding a X.509 certificate-based digital signature to a PDF document in PKCS#7 format via the Sign method of the PdfDocument object.
8.3.1 Support for Certificate-based Cryptography in .NET
To create a digitally signed document, or sign an existing PDF, AspPDF.NET needs to obtain an instance of the X509Certificate2 object (System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates namespace.) Certificates usually reside in "certificate stores". The following code snippet obtains a certificate by its subject name from the "ROOT" certificate store residing in the "local machine" section of the server's storage:
using System.Security.Cryptography.Pkcs;
using System.Security.Cryptography.X509Certificates;
...
X509Store objStoreMy = new X509Store( StoreName.Root, StoreLocation.LocalMachine );
objStoreMy.Open(OpenFlags.ReadOnly);
X509Certificate2Collection objCertColl =
objStoreMy.Certificates.Find( X509FindType.FindBySubjectName,
"Persits Software", false );
X509Certificate2 objCert = objCertColl[0];
The objCert object thus obtained can now be passed directly to the PdfDocument.Sign method for AspPDF.NET to perform the digital signing of the document.
Digital signing is often a tricky process as it involves private keys that are inherently secure entities. The code shown above, when run in an ASP.NET environment, will not produce an error but an attempt to use the certificate in the Sign method probably will, as we are now trying to access the private key and causing a security violation. To avoid the error, "user impersonation" may be required. The PdfManager object offers the LogonUser method which impersonates an arbitrary user account. The method expects the domain name (or an empty string if this is a local domain), username and password as arguments. Call this method before calling the certificate-store methods, as follows:
X509Store objStoreMy = new X509Store( StoreName.Root, StoreLocation.LocalMachine );
...
The signer certificate does not have to reside in a certificate store, it can also be obtained directly from a password-protected .pfx file (PKCS#12 format). An instance of the X509Certificate2 object is created by calling its constructor and passing the .pfx file path and password as arguments. Note that in a ASP.NET environment you must call LogonUser before creating the certificate object this way, or the signing will fail. For example:
X509Certificate2 objCert = new X509Certificate2( @"c:\path\mycert.pfx", "my_password" );
...
For more general information about X509 certificates, visit the AspEncrypt.com site.
8.3.2 Sign Method
The Sign method expects a instance of the X509Certificate2 object with its HasPrivateKey property set to true. It also accepts the signer name, reason for signing, and location arguments (the first one is required, the other two are optional), and also an optional parameter string or parameter object controlling the visibility and location of the signature field within the document.
The following code sample adds a signature to a PDF document:
NOTE: A digitally signed document can only be saved to disk (via the Save method). Saving to memory or an HTTP stream cannot be used once Sign is called, and an attempt to call SaveToMemory or SaveHttp will result in an error exception.
UPDATE: As of Version 2.7, a signed document can be saved to disk and memory, but not to an HTTP stream.
8.3.3 Visible Signatures
By default, the Sign method creates an invisible signature. Using the last optional argument of the Sign method, it is possible to specify a page and location within that page where the signature icon is to appear.
The following code fragment draws a signature icon in the upper-left corner of the first page of the document (middle arguments omitted for brevity):
It is also possible to change the default appearance of a signature by drawing on the canvas of a PdfAnnot object returned by the Sign method. Annotations are described in detail in Chapter 10.
AspPDF.NET's digital signature functionality would not be complete without a way to verify an existing signature in a document.
Signature verification is implemented via the VerifySignature method of the PdfDocument object. VerifySignature can only be called on an instance of PdfDocument created via OpenDocument (the latter is described in detail in Chapter 9.) VerifySignature does not take any arguments.
VerifySignature returns null if no PKCS#7 signatures are found in the document. Otherwise, it returns an instance of the PdfSignature object encapsulating various property of the signature, including its validation status (valid/invalid), signer name, reason for signing, location, and other information. If a document contains multiple signatures (such as, when an already signed document was signed again), the VerifySignature method validates and returns the one that covers the largest portion of the document, which is usually the latest signature.
The following code fragment opens a PDF document from a file, and attempts to validate a signature, if one is present:
PdfSignature objSig = objDoc.VerifySignature();
if( objSig == null )
{
Console.WriteLine( "No signature found." );
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine( "Status = " + objSig.Status );
Console.WriteLine( "Name = " + objSig.Name );
Console.WriteLine( "Reason = " + objSig.Reason );
Console.WriteLine( "Contents = " + objSig.Contents );
}
Server-side digital signing is demonstrated by Live Demo #17:
8.4 Client-Side Signing of Server-Side PDFs
The PdfDocument.Sign method described in the previous section requires access to both the PDF document being signed and the private key of the certificate used for signing. In most cases, this means the signer certificate has to be transferred to the server, which may be undesirable as the security of the private key is jeopardized.
Version 3.4 of AspPDF.NET introduces a new, secure way of signing PDF documents in which the document being signed never leaves the server, while the signer certificate never leaves the client machine: the hash value and signature do all the traveling. The actual signing takes place on the client workstation using Version 2.9+ of the XEncrypt ActiveX control (included with the Persits AspEncrypt component.) Since an ActiveX control is involved, the user is required to run Internet Explorer on Windows.
From the user's prospective, the entire signing process can be completed with a single button click, but under the hood there are three distinct steps involved: server-side pre-signing, client-side signing, and server-side signature injection. Below is the detailed description of these three steps:
Step 1: Server-Side Pre-Signing
During pre-signing, a new document is created which looks almost completely like a real signed document but the "signature" embedded in it just contains a bunch of 0's. This sequence of 0's is merely a placeholder which will eventually contain the real signature (see Step 3). Also the SHA hash value of the appropriate parts of the document is computed. This hash value will be transferred to the client workstation for signing in Step 2.
Pre-signing is performed by calling the PdfDocument.Sign method with the first argument (X509Certificate2 object) simply set to null, followed by a call to PdfDocument.Save to create the pre-signed document. The parameter BinarySize must be specified when calling Sign. This parameter specifies the size of the signature placeholder. The value of 5000 is usually sufficient but may need to be higher in some cases. The code sample below performs signature size validation and alerts the user if the space allocated for the signature is insufficient.
The SHA hash value of the relevant parts of the document along with signature location and size are returned by the property PdfDocument.SignatureInfo in the form of a comma-separated list. The 1st item on the list is a HEX-encoded SHA value. The 2nd item is the signature location within the document (this number is used in Step 3.) The 3rd item is the signature placeholder's size which matches the BinarySize parameter. The SignatureInfo property can only be called after the Save method has been called. For example:
PdfDocument objDoc = objPDF.OpenDocument( Server.MapPath("DocToSign.pdf") );
objDoc.Sign( null, Request["name"], Request["reason"], Request["location"],
"BinarySize=5000; visible=true; x=10, y=700; width=50; height=50; pageindex=1; print=true" );
objDoc.Save( Server.MapPath( "files\\" + Session.SessionID + ".pdf" ), false );
objDoc.Close();
Response.Write( objDoc.SignatureInfo );
This code will display a value similar to this:
Step 2: Client-Side Signing
The hash value obtained in Step 1 is transferred to the client workstation for signing with the user's personal certificate. The actual signing is performed with the help of Persits XEncrypt, the client-side ActiveX control included with Persits AspEncrypt. Version 2.9+ of XEncrypt implements the method CryptoMessage.SignHash which produces the PKCS#7 signature of a SHA hash value. This ActiveX control is also capable of presenting the user with a list of certificates to choose from in case the user has more than one on his/her workstation. Since an ActiveX control is involved in this operation, the Microsoft IE browser on Windows is required.
The following client-side JavaScript code snippet performs client-side signing of a hash value:
var Msg = Context.CreateMessage( true );
Msg.SetSignerCert( Cert );
var HashBlob = XEncrypt.CreateBlob();
HashBlob.Hex = Hash;
var PKCS7Blob = Msg.SignHash( HashBlob );
txtSignature = PKCS7Blob.Hex;
Finally, the PKCS#7 signature generated by the CryptoMessage.SignHash method in Step 2 is transferred to the server and injected into the pre-signed file created during Step 1. This operation is performed using the PdfManager.InjectTextIntoFile method. This method expects three arguments: the path to the file, the text being injected (Hex-encoded PKCS#7 signature in our case) and the location within the file where text is to be written. The signature location is obtained in Step 1 via the PdfDocument.SignatureInfo property. The InjectTextIntoFile method returns the filename (without the path) of the file being injected.
The following code snippet demonstrates this final step:
string strFilename = objPDF.InjectTextIntoFile( Request["Path"], Request["Signature"], int.Parse(Request["Location"]) );
Response.Write( strFilename );
The following code sample implements the three-step process described above via two AJAX calls: the first AJAX call invokes the sever-side pre-signing script demo_clientsign_obtainhash.asp/.aspx and transfers the hash value (along with other useful information) to the user workstation for signing. After the hash value is signed, a 2nd AJAX call transfers the PKCS#7 signature (along with other useful information) to the server and invokes the signature injection script demo_clientsign_injectsignature.asp/.aspx.
In addition to the hash value and signature, the scripts pass around the signature location, signature size and the full path of the pre-signed PDF file. The signature size value is used by the client-side JavaScript to ensure the actual signature size does not exceed the size of the signature placeholder, and alerts the user if it does. The signature location and file path are sent to the client side via the 1st AJAX call merely to be sent back via the 2nd AJAX call -- they are not used by the client-side JavaScript for any other purpose.
Also, in case the user does not have a valid certificate for signing, or chooses to cancel the signing operation by not selecting a certificate from the list, the 2nd AJAX call contains a "delete" command which causes the pre-signed PDF file to be deleted since there is no point in preserving a file with an incomplete (and invalid) signature.
demo_clientsign_ajax.js:
var txtHashEtc, txtSignature;
var strObtainHashFilename = 'demo_clientsign_obtainhash.asp';
var strInjectSignatureFilename = 'demo_clientsign_injectsignature.asp';
function GetXmlObject()
{
var xmlHttp = null;
try
{
// Firefox, Opera 8.0+, Safari
xmlHttp=new XMLHttpRequest();
}
catch (e)
{
// Internet Explorer
try
{
xmlHttp=new ActiveXObject('Msxml2.XMLHTTP');
}
catch (e)
{
xmlHttp=new ActiveXObject('Microsoft.XMLHTTP');
}
}
return xmlHttp;
}
function SetASPX()
{
strObtainHashFilename = 'demo_clientsign_obtainhash.aspx';
strInjectSignatureFilename = 'demo_clientsign_injectsignature.aspx';
}
function Sign()
{
xmlHttp = GetXmlObject();
if( xmlHttp==null )
{
alert ('Your browser does not support AJAX!');
return;
}
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = stateChanged;
// STEP1: Send signature attributes to server, obtain hash
if( document.forms[0].txtName.value == '' )
{
alert( 'Name must be specified.' );
document.forms[0].txtName.focus();
return;
}
if( document.forms[0].txtReason.value == '' )
{
alert( 'Reason for signing must be specified.' );
document.forms[0].txtReason.focus();
return;
}
if( document.forms[0].txtLocation.value == '' )
{
alert( 'Location must be specified.' );
document.forms[0].txtLocation.focus();
return;
}
var strParams;
strParams = 'name=' + encodeURIComponent( document.forms[0].txtName.value );
strParams += '&reason=' + encodeURIComponent( document.forms[0].txtReason.value );
strParams += '&location=' + encodeURIComponent( document.forms[0].txtLocation.value );
strParams += '&rnd=' + Math.random(); // to prevent caching
xmlHttp.open('GET', strObtainHashFilename + '?' + strParams, true);
xmlHttp.send(null);
}
function stateChanged()
{
if( xmlHttp.readyState == 4 )
{
var strResponse;
strResponse = xmlHttp.responseText;
// check for run-time errors that may occur in the server-side script
if( strResponse.search('error' ) != -1 )
{
alert( 'An error occurred while obtaining hash value: ' + strResponse );
return;
}
// Save hash, location and path
txtHashEtc = strResponse;
// Invoke signing function
setTimeout( ComputeSignature, 0 );
}
}
// Uses XEncrypt ActiveX control to sign the hash
function ComputeSignature()
{
// Split signature info into hash, signature location, size and file path
var SigInfo = txtHashEtc.split( ',' );
var Hash = SigInfo[0];
var Location = SigInfo[1];
var Size = SigInfo[2];
var Path = SigInfo[3];
try
{
// Open "MY" certificate store which contains client certs
var Store = XEncrypt.OpenStore('MY', false );
// Does the store contain certificates?
var Count = Store.Certificates.Count;
if( Count == 0 )
{
alert( 'You have no certificates.' );
DeletePDFFile( Path );
return;
}
// If store contains more than one, enable user to pick one
var Cert = null;
if( Count > 1 )
{
Cert = XEncrypt.PickCertificate(Store, 4+8+16,
'Select signer certificate',
'This certificate\'s private key will be used for signing' );
if( Cert == null )
{
DeletePDFFile( Path );
return;
}
}
else
{
// otherwise just pick that only one cert
Cert = Store.Certificates(1)
}
// Make sure the cert has a private key associated with it
if( !Cert.PrivateKeyExists )
{
alert( 'This certificate has no private key associated with it.' );
DeletePDFFile( Path );
return;
}
var Context = XEncrypt.OpenContext( '', false );
var Msg = Context.CreateMessage( true );
Msg.SetSignerCert( Cert );
var HashBlob = XEncrypt.CreateBlob();
HashBlob.Hex = Hash;
var PKCS7Blob = Msg.SignHash( HashBlob );
if( PKCS7Blob.Length > Size )
{
alert( 'Signature size exceeds the space allocated for it. Contact technical support.' );
DeletePDFFile( Path );
return;
}
txtSignature = PKCS7Blob.Hex;
}
catch(err)
{
alert( 'An error occurred during digital signing: ' + err.message );
DeletePDFFile( Path );
return;
}
// Send signature and other info to server
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = stateChanged2;
var strParams;
strParams = 'path=' + encodeURIComponent( Path );
strParams += '&location=' + encodeURIComponent( Location );
strParams += '&signature=' + encodeURIComponent( txtSignature );
// Use POST method as the signature is a long string
xmlHttp.open('POST', strInjectSignatureFilename, true);
xmlHttp.setRequestHeader('Content-type', 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
xmlHttp.send(strParams);
}
function stateChanged2()
{
if( xmlHttp.readyState == 4 )
{
var strResponse;
strResponse = xmlHttp.responseText;
// check for run-time errors that may occur in the server-side script
if( strResponse.search('error' ) != -1 )
{
alert( 'An error occurred while comlpeting the signing: ' + strResponse );
return;
}
document.getElementById('divLink').innerHTML = 'Success! Download the signed file from ' + strResponse + '';
}
}
function DeletePDFFile( Path )
{
xmlHttp.onreadystatechange = stateChanged3;
var strParams;
strParams = 'delete=1&path=' + encodeURIComponent( Path );
strParams += '&rnd=' + Math.random(); // to prevent caching
xmlHttp.open('GET', strInjectSignatureFilename + '?' + strParams, true);
xmlHttp.send(null);
}
function stateChanged3()
{
if( xmlHttp.readyState == 4 )
{
var strResponse;
strResponse = xmlHttp.responseText;
// check for run-time errors that may occur in the server-side script
if( strResponse.search('error' ) != -1 )
{
alert( 'An error occurred while deleting the temporary file: ' + strResponse );
return;
}
}
}
demo_clientsign.cs.aspx:
classid="CLSID:F9463571-87CB-4A90-A1AC-2284B7F5AF4E"
codeBase="aspencrypt.dll#VERSION=2,9,0,0"
id="XEncrypt">
</OBJECT>
<form id="SigningForm" runat="server">
<table border="1">
<tr><td>Name:</td><td><asp:textbox runat="server" id="txtName" size="40"/></td></tr>
<tr><td>Reason for signing:</td><td><asp:textbox runat="server" id="txtReason" size="40"/></td></tr>
<tr><td>Location:</td><td><asp:textbox runat="server" id="txtLocation" size="40"/></td></tr>
<tr><td colspan="2" align="center">
<asp:button runat="server"
id="TheButton" Text="Sign this server-side PDF" onclientclick="Sign(); return false;"/>
</td></tr>
</table>
<p>
<asp:label runat="server" id="divLink"/>
</form>
demo_clientsign_obtainhash.cs.aspx:
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Reflection" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="Persits.PDF" %>
<script runat="server" LANGUAGE="C#">
void Page_Load(Object Source, EventArgs E)
{
// Pre-signs the PDF document:
// - Creates a placeholder inside it to contain the signature
// - Obtains the hash value of the signable area, as well as the signature location
PdfManager objPDF = new PdfManager();
PdfDocument objDoc = objPDF.OpenDocument( Server.MapPath("DocToSign.pdf") );
// Pre-sign: null is passed as the first argument to Sign method
PdfAnnot objAnnot = objDoc.Sign( null, Request["name"], Request["reason"], Request["location"],
"BinarySize=5000;visible=true;x=10,y=700;width=50;height=50;pageindex=1;print=true" );
// Give the signature the appearance of an image
PdfImage objImage = objDoc.OpenImage( Server.MapPath( "signature.png" ) );
PdfGraphics objGraph = objDoc.CreateGraphics( "Left=0; Bottom=0; Right=53; Top=53" );
objGraph.Canvas.DrawImage( objImage, "x=0; y=0" );
objAnnot.Graphics[0] = objGraph;
objDoc.Save( Server.MapPath( "files\\" + Session.SessionID + ".pdf" ), false );
objDoc.Close();
Response.Write( objDoc.SignatureInfo );
Response.Write( "," + objDoc.Path );
}
</script>
demo_clientsign_injectsignature.cs.aspx:
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Reflection" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.IO" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="Persits.PDF" %>
<script runat="server" LANGUAGE="C#">
void Page_Load(Object Source, EventArgs E)
{
if( Request["delete"] != null )
{
File.Delete( Request["Path"] );
}
else
{
PdfManager objPDF = new PdfManager();
string strFilename = objPDF.InjectTextIntoFile( Request["Path"],
Request["Signature"], int.Parse(Request["Location"]) );
Response.Write( strFilename );
}
}
</script>
demo_clientsign.vb.aspx:
classid="CLSID:F9463571-87CB-4A90-A1AC-2284B7F5AF4E"
codeBase="aspencrypt.dll#VERSION=2,9,0,0"
id="XEncrypt">
</OBJECT>
<form id="SigningForm" runat="server">
<table border="1">
<tr><td>Name:</td><td><asp:textbox runat="server" id="txtName" size="40"/></td></tr>
<tr><td>Reason for signing:</td><td><asp:textbox runat="server" id="txtReason" size="40"/></td></tr>
<tr><td>Location:</td><td><asp:textbox runat="server" id="txtLocation" size="40"/></td></tr>
<tr><td colspan="2" align="center">
<asp:button runat="server" id="TheButton"
Text="Sign this server-side PDF" onclientclick="SetVBNet();Sign();return false;"/>
</td></tr>
</table>
<p>
<asp:label runat="server" id="divLink"/>
</form>
demo_clientsign_obtainhash.vb.aspx:
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Reflection" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="Persits.PDF" %>
<script runat="server" LANGUAGE="VBScript">
Sub Page_Load(Source As Object, E As EventArgs)
' Pre-signs the PDF document:
' - Creates a placeholder inside it to contain the signature
' - Obtains the hash value of the signable area, as well as the signature location
Dim objPDF As PdfManager = new PdfManager()
Dim objDoc As PdfDocument = objPDF.OpenDocument( Server.MapPath("DocToSign.pdf") )
' Pre-sign: null is passed as the first argument to Sign method
Dim objAnnot As PdfAnnot = objDoc.Sign( Nothing, _
Request("name"), Request("reason"), Request("location"), _
"BinarySize=5000;visible=true;x=10,y=700;width=50;height=50;pageindex=1;print=true" )
' Give the signature the appearance of an image
Dim objImage As PdfImage = objDoc.OpenImage( Server.MapPath( "signature.png" ) )
Dim objGraph As PdfGraphics = objDoc.CreateGraphics( "Left=0; Bottom=0; Right=53; Top=53" )
objGraph.Canvas.DrawImage( objImage, "x=0; y=0" )
objAnnot.Graphics(0) = objGraph
objDoc.Save( Server.MapPath( "files\" + Session.SessionID + ".pdf" ), false )
objDoc.Close()
Response.Write( objDoc.SignatureInfo )
Response.Write( "," + objDoc.Path )
End Sub
</script>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.Reflection" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="System.IO" %>
<%@ Import Namespace="Persits.PDF" %>
<script runat="server" LANGUAGE="VBScript">
Sub Page_Load(Source As Object, E As EventArgs)
If Not Request("delete") Is Nothing Then
File.Delete( Request("Path") )
Else
Dim objPDF As PdfManager = new PdfManager()
Dim strFilename As String = objPDF.InjectTextIntoFile( _
Request("Path"), Request("Signature"), Int32.Parse(Request("Location") ) )
Response.Write( strFilename )
End If
End Sub
</script>
To test this application, go to Live Demo #18.
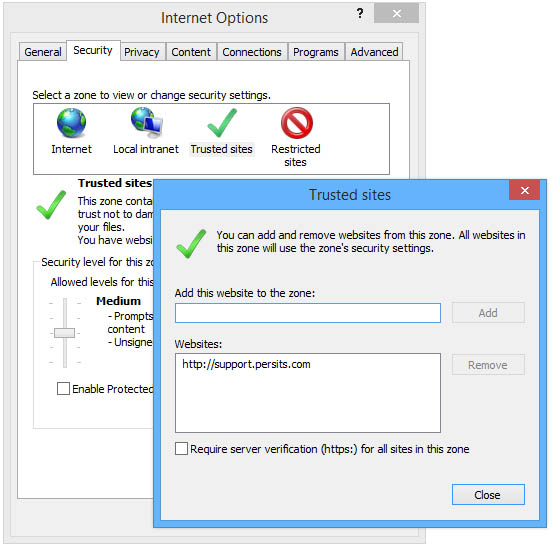
To avoid an Access is Denied error during signing, run IE as Administrator or add https://support.persits.com to the list of Trusted sites as shown on the following image.
8.5 PDF-based Secure Mail
Some web applications require that the users be periodically sent sensitive information via email securely. Persits Software, Inc., the maker of AspPDF and AspPDF.NET, offers certificate-based secure email functionality via the components AspEmail and AspEncrypt.
In order to receive and decrypt secure email, the recipient needs to have acquired a personal certificate from a certification authority such as Comodo. The public-key portion of the certificate needs to be exported to a file and placed on the web sever generating the secure email. Also, the recipient must use stand-alone S/MIME-enabled email software to decrypt and read the messages such as Outlook, Thunderbird, etc. Web-based email services such as gmail, hotmail, etc. cannot be used.
PDF format offers an alternative to certificate-based email in which the secure content is embedded in a password-protected PDF document and sent to the user as an attachment via regular, unencrypted, email. Upon the receipt of the message, the user opens the attachment with Acrobat Reader and enters his password to view the content.
PDF is a great vehicle for delivering secure email for the following reasons:
- it supports strong 128-bit and 256-bit password-based encryption;
- it provides a means for file attachments via special interactive objects called annotations described in Chapter 10.
- it is platform-independent;
- it does not require special software other than a PDF viewer such as Acrobat Reader;
- it does not require a digital certificate;
- it can be used with any stand-alone and web-based email reader.
PDF-based secure message functionality is demonstrated by the following AspPDF.NET live demo: